Food, clothing, plastic, and other items used in our daily lives become less expensive after being recycled. This waste is called waste.
Waste is not just garbage; if handled correctly, it can be repurposed into food or other useful materials. Proper waste management not only protects our environment but also makes life cleaner and healthier. If the environment is not managed properly, waste can harm human health and the overall balance of nature. Therefore, effective waste management is essential in today’s world.
In this blog, we will explore the different types of waste, their proper management, the 5 main types of waste management, and how organizations like Kumar Engineering are contributing with innovative solutions like food waste composters.
What is Waste?
Waste refers to any material, substance, or by-product that is no longer useful, wanted, or needed by the person or process generating it. It is typically discarded because it has served its intended purpose, is spoiled, or is no longer functional. Waste can originate from homes, industries, agriculture, hospitals, offices, or any human activity.
Definition of Waste
Waste refers to unwanted or unusable materials that are left over after a process, activity, or use. It can come from households, industries, hospitals, agriculture, or businesses.
Examples of Waste
- Dirty water and industrial by-products
- Food scraps, vegetable peels, and leftovers from the kitchen
- Plastic bottles, wrappers, and packaging materials
- Old electronic items like mobiles and computers
- Chemicals, paints, and medical disposables
Types of Waste
Waste can be classified into several categories:
- Solid Waste – Household garbage, packaging, plastics, papers, glass, and metals.
- Liquid Waste – Sewage, dirty water, chemicals, and industrial wastewater.
- Organic Waste – Food scraps, garden waste, and agricultural waste that can be composted.
- Hazardous Waste – Chemicals, paints, pesticides, and items harmful to humans or the environment.
- Biomedical Waste – Hospital and clinical waste like syringes, bandages, surgical items, and medicines.
- E-Waste – Discarded electronic products such as mobile phones, computers, and appliances.
WHO Biomedical Waste Management
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), biomedical waste is any waste that contains infectious materials. It includes items like needles, surgical gloves, blood bags, diagnostic samples, and medicines.
WHO Guidelines for Biomedical Waste Management:
- Segregation at Source – Waste must be separated into color-coded bins (yellow, red, blue, black) depending on type.
- Collection & Storage – Waste should be collected safely in closed containers to prevent infection spread.
- Treatment – Techniques like autoclaving, microwaving, or incineration are used to destroy harmful pathogens.
- Final Disposal – After treatment, waste is safely disposed of in landfills or reused if possible.
5 Types of Waste Management
Waste management is not a single process but a combination of multiple approaches. Here are the 5 types of waste management:
1. Recycling
Recycling is the process of converting used materials like paper, glass, metal, and plastics into new products. It reduces raw material consumption and saves energy. For example, recycling aluminum cans saves 95% of the energy compared to making them from raw materials.
2. Composting
Composting is a natural process of converting organic waste like food scraps, garden waste, and agricultural residues into nutrient-rich compost. This method improves soil health and reduces landfill pressure.
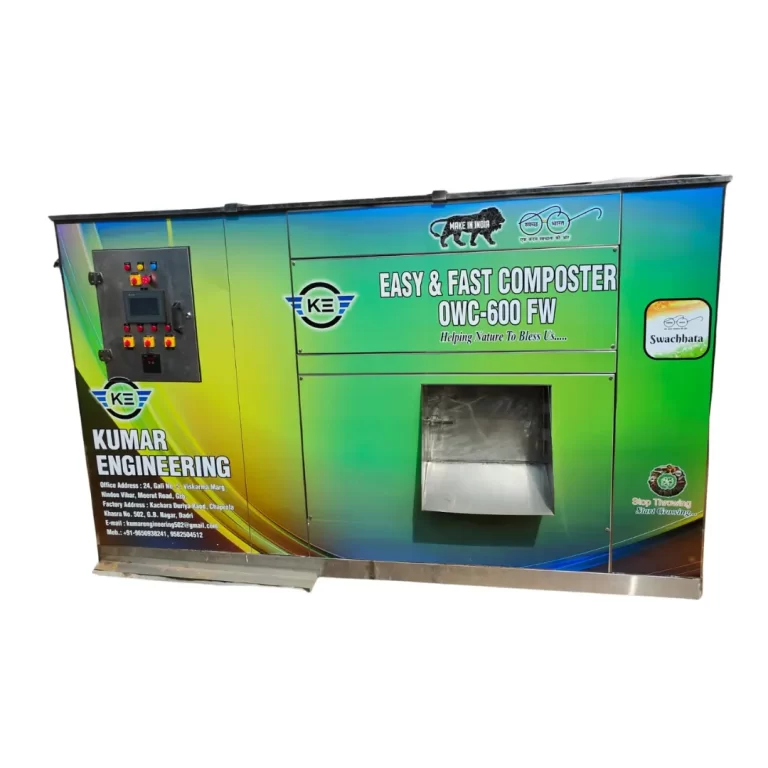
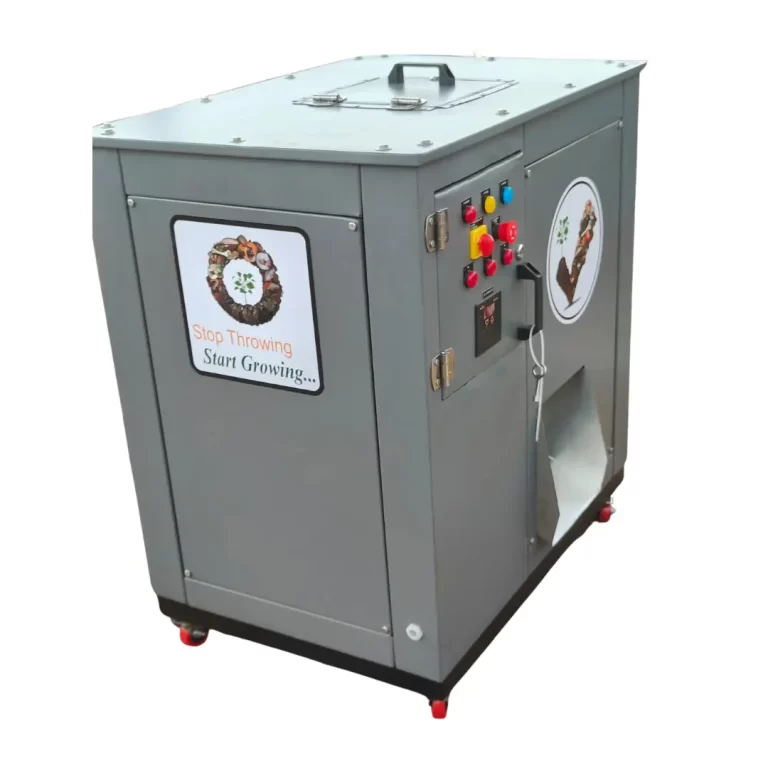
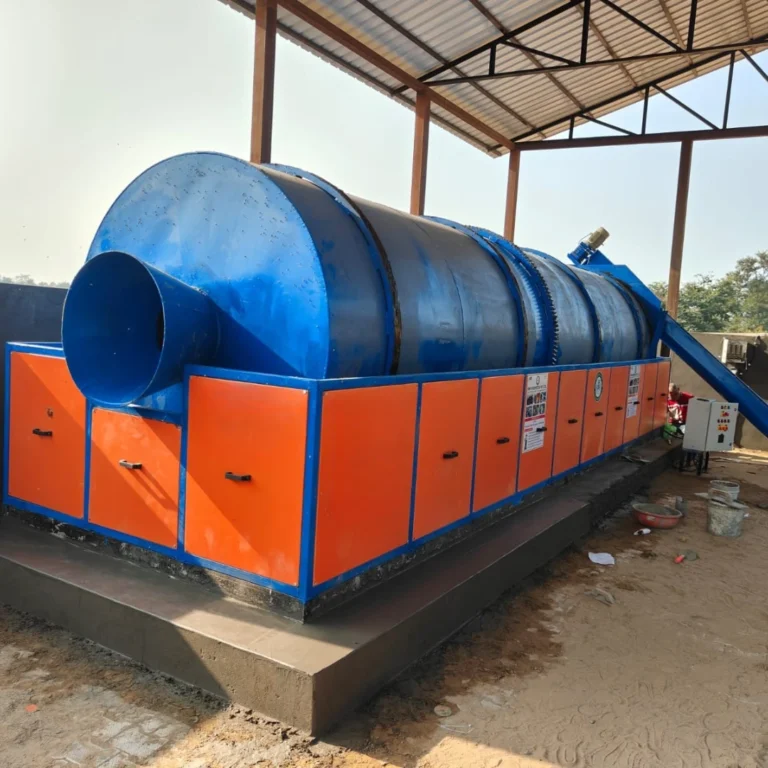
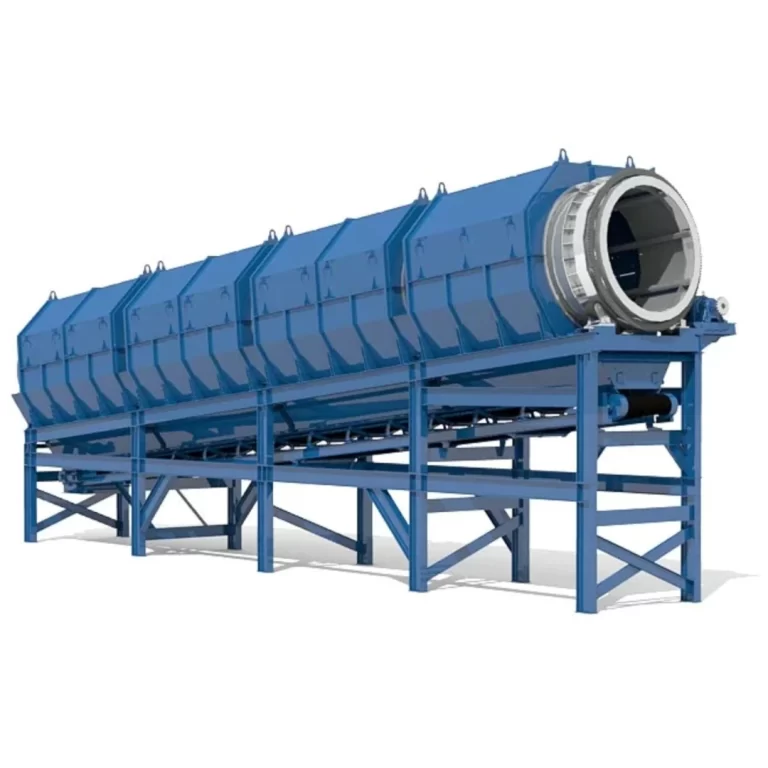
This is where Kumar Engineering plays a vital role. As a leading food waste composter manufacturer, they provide advanced machines that can turn large volumes of food waste into usable compost within hours. Their eco-friendly composters are widely used by hotels, restaurants, societies, and industries to manage food waste efficiently.
3. Landfills
Landfills are one of the most common waste disposal methods where waste is buried under the ground. However, modern sanitary landfills are designed with protective liners and systems to prevent soil and water contamination.
4. Incineration
Incineration involves burning waste at very high temperatures. This method reduces the volume of waste significantly and is often used for hazardous and biomedical waste. However, it must be done with proper pollution control to avoid harmful emissions.
5. Waste-to-Energy
This method involves converting non-recyclable waste into usable energy through processes like pyrolysis, gasification, and anaerobic digestion. It helps reduce landfill waste and also generates renewable energy.
Conclusion
Waste is inevitable, but mismanagement is preventable. In this blog we explore about 5 types of waste management like recycling, composting, incineration, landfills, and waste-to-energy systems and hope this is helpful to reduce environmental impact and build a healthier society.
From managing biomedical waste under World Health Organization guidelines to promoting the five major types of waste management, every effort is important towards sustainability. And when it comes to food waste management, Kumar Engineering has set a standard with its advanced food waste composting machine and horticulture waste composters that convert food waste into useful fertilizer.